Cloud data warehousing sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with originality from the outset. In the realm of modern businesses, the adoption of cloud data warehousing has become a pivotal strategy for efficient data management and analysis.
As we delve deeper into the architecture, differences from traditional methods, best practices, and FAQs surrounding cloud data warehousing, a comprehensive understanding of this revolutionary technology will emerge.
Introduction to Cloud Data Warehousing

Cloud data warehousing refers to the process of storing and managing data in a cloud-based platform, allowing businesses to access and analyze large volumes of data in a scalable and cost-effective manner. This technology has become increasingly popular in modern businesses due to its numerous advantages over traditional data warehousing methods.
Importance of Cloud Data Warehousing
Cloud data warehousing plays a crucial role in enabling businesses to harness the power of big data and analytics. By moving data to the cloud, organizations can benefit from enhanced flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. This allows for real-time data processing, improved decision-making, and the ability to quickly adapt to changing business needs.
- Scalability: Cloud data warehousing offers the flexibility to scale up or down based on data storage and processing requirements, eliminating the need for costly infrastructure investments.
- Cost-effectiveness: By utilizing cloud-based solutions, businesses can reduce operational costs associated with maintaining on-premises data warehouses, such as hardware maintenance and upgrades.
- Accessibility: Cloud data warehousing provides easy access to data from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote collaboration and streamlined data sharing among team members.
Key Benefits of Cloud Data Warehousing
- Enhanced Performance: Cloud data warehouses are designed to handle large volumes of data and complex queries efficiently, resulting in faster data processing and analysis.
- Data Security: Cloud data warehousing providers implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Data Integration: Cloud data warehousing solutions offer seamless integration with various data sources and applications, enabling businesses to consolidate and analyze data from multiple sources in one centralized location.
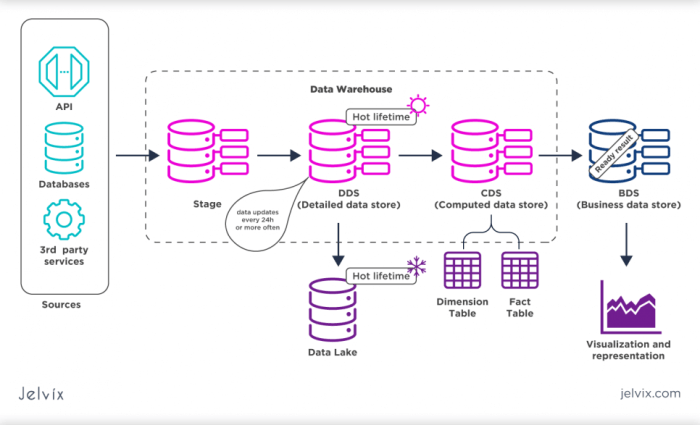
Architecture of Cloud Data Warehousing

In a cloud data warehousing system, the architecture typically consists of several key components working together to store, process, and access data efficiently and securely.
Components of Cloud Data Warehousing Architecture
- Data Sources: These are the various systems and applications that generate data to be stored in the data warehouse.
- Data Ingestion Tools: Tools that help in extracting and loading data from different sources into the cloud data warehouse.
- Data Storage: The actual storage infrastructure where the data is housed, which can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
- Data Processing: This component involves transforming, cleaning, and organizing the data for analysis and reporting.
- Data Access Tools: Tools that enable users to query, visualize, and analyze the data stored in the cloud data warehouse.
- Security and Compliance: Measures put in place to ensure the security and compliance of the data stored in the cloud data warehouse.
Data Storage, Processing, and Access in Cloud Data Warehousing
In a cloud data warehouse, data is stored in a highly scalable and distributed manner, utilizing cloud storage solutions like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Microsoft Azure Blob Storage. This allows for flexible storage capacity and cost-effective scalability.
When it comes to processing data, cloud data warehouses use massively parallel processing (MPP) architectures to handle large volumes of data efficiently. This involves breaking down queries into smaller parts that can be processed in parallel across multiple nodes or clusters.
For data access, users can interact with the cloud data warehouse through various tools and interfaces, such as SQL queries, business intelligence tools, or data visualization platforms. These tools allow users to extract insights and make data-driven decisions based on the data stored in the warehouse.
Differences Between Cloud Data Warehousing and Traditional Data Warehousing
Cloud data warehousing and traditional data warehousing are two distinct approaches to managing and analyzing large volumes of data. Let’s explore the key differences between these two methods and examine the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Scalability and Flexibility
One of the primary differences between cloud data warehousing and traditional data warehousing is scalability. Cloud data warehousing solutions offer the ability to easily scale resources up or down based on demand. This means that organizations can quickly adjust their storage and processing capabilities to accommodate changing data volumes. In contrast, traditional data warehousing systems often require significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, making it challenging to scale resources dynamically.
Cost Efficiency
Cloud data warehousing is often more cost-effective than traditional data warehousing. With cloud solutions, organizations can avoid the high upfront costs associated with purchasing and maintaining on-premises hardware. Instead, they can pay for storage and processing on a consumption basis, only paying for the resources they use. This pay-as-you-go model can result in significant cost savings for organizations, especially those with fluctuating data processing needs.
Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud data warehousing offers greater accessibility and collaboration capabilities compared to traditional data warehousing. With cloud solutions, data can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing for remote work and collaboration among team members. Traditional data warehousing systems, on the other hand, may be limited to on-site access, restricting the ability to work with data remotely.
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance considerations differ between cloud data warehousing and traditional data warehousing. While cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect data, some organizations may have concerns about storing sensitive information in the cloud. Traditional data warehousing systems offer more control over data storage and security, which may be preferred by organizations with strict compliance requirements or sensitive data.
Data Processing Speed
Cloud data warehousing typically offers faster data processing speeds than traditional data warehousing systems. With cloud solutions, organizations can leverage distributed computing resources to process data more quickly and efficiently. This can lead to faster insights and decision-making, giving organizations a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Overall, cloud data warehousing has revolutionized data management practices by offering scalability, cost efficiency, accessibility, and enhanced processing speeds. While traditional data warehousing systems have their advantages, the flexibility and capabilities of cloud solutions make them an attractive option for organizations looking to modernize their data infrastructure.
Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Data Warehousing

Implementing a cloud data warehouse requires careful planning and consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and scalability. Below are some best practices to guide you through the process:
Choosing the Right Cloud Data Warehousing Solution
When selecting a cloud data warehousing solution, it is important to consider factors such as:
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can easily scale with your growing data needs without compromising performance.
- Integration Capabilities: Look for a platform that seamlessly integrates with your existing systems and tools to facilitate data migration and management.
- Data Security: Prioritize solutions that offer robust security features to protect your sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the pricing structure of different providers and choose a solution that aligns with your budget while meeting your requirements.
Optimizing Performance and Scalability
To optimize performance and scalability in a cloud data warehouse environment, consider the following tips:
- Partitioning Data: Partition your data to distribute workloads evenly and improve query performance.
- Indexing: Use indexing to speed up data retrieval and enhance query efficiency.
- Data Compression: Implement data compression techniques to reduce storage costs and improve query processing speeds.
- Data Distribution: Distribute data across multiple nodes to enhance parallel processing and boost performance.
In conclusion, cloud data warehousing stands as a beacon of innovation in the realm of data storage and management. By embracing this technology, businesses can unlock new possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced decision-making processes in the digital age.