Data governance for enterprises sets the foundation for maintaining data integrity and compliance within organizations. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decisions, implementing a robust data governance framework becomes imperative. This article delves into the key components, implementation strategies, tools, and regulatory aspects of data governance for enterprises.
Overview of Data Governance for Enterprises
Data governance in the context of enterprises refers to the framework and processes put in place to ensure the effective management and protection of a company’s data assets. It involves defining policies, procedures, and roles to ensure data quality, security, compliance, and usability.
Effective data governance is crucial for businesses as it helps in maintaining data integrity, improving decision-making processes, managing risks, and ensuring regulatory compliance. By implementing data governance practices, enterprises can enhance data quality, reduce data-related errors, and increase overall operational efficiency.
Importance of Data Governance for Businesses
Data governance is essential for businesses to maintain data integrity and ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and trustworthy. It helps in establishing a single source of truth for data, which can be crucial for making informed business decisions. Additionally, data governance ensures compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or other industry-specific requirements.
- Enhances data quality and accuracy
- Improves decision-making processes
- Reduces operational risks
- Ensures regulatory compliance
Implementing data governance practices can lead to cost savings, increased revenue, and improved customer satisfaction.
Examples of Effective Data Governance Benefits for Enterprises
- Improved Customer Relationship Management (CRM): By ensuring accurate and up-to-date customer data through data governance, enterprises can personalize customer interactions, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced Data Security: Data governance helps in defining access controls, encryption standards, and data protection policies, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyber threats.
- Better Decision-Making: With reliable and consistent data available through data governance, enterprises can make informed decisions based on accurate insights, leading to improved business outcomes.
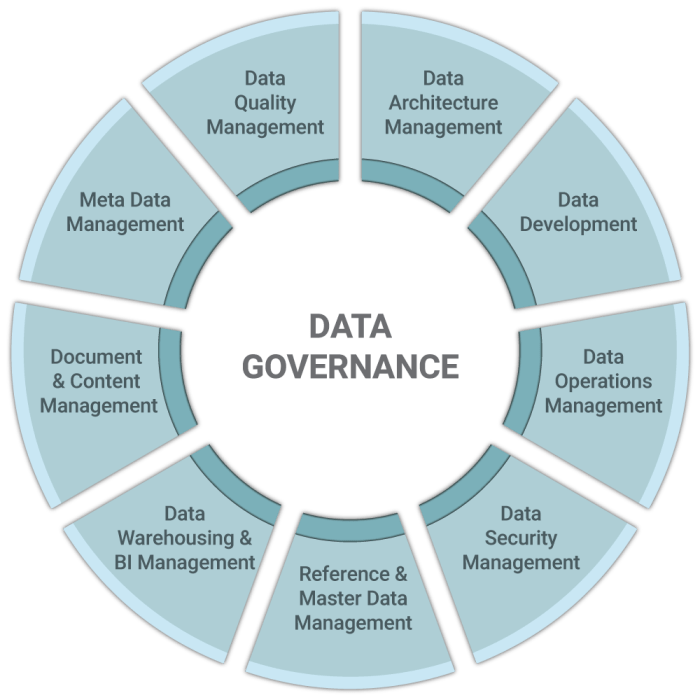
Components of Data Governance
Data governance is a critical process for enterprises to ensure the proper management, protection, and utilization of their data assets. A robust data governance framework consists of several key components that work together to establish guidelines and procedures for handling data effectively.
Key Components of a Robust Data Governance Framework
- Data Stewardship: Assigning responsibilities to individuals or teams to oversee data management processes and ensure compliance with data governance policies.
- Data Quality Management: Implementing processes to monitor, assess, and improve the quality of data to enhance decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Data Security: Establishing protocols and mechanisms to protect data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring compliance with regulations and policies to safeguard sensitive or personal data from misuse or unauthorized disclosure.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Managing the entire lifecycle of data from creation to archival or disposal to maintain data integrity and relevance.
Role of Policies and Procedures in Data Governance
Policies and procedures form the foundation of a data governance framework by defining rules, standards, and guidelines for managing and using data within an organization. They provide a structured approach to data governance and help ensure consistency, transparency, and accountability in data-related activities. Policies establish the principles and objectives of data governance, while procedures Artikel the specific steps and actions to be followed in implementing those policies.
Significance of Data Quality Management within Data Governance Practices, Data governance for enterprises
Data quality management is a critical component of data governance as it directly impacts the reliability, accuracy, and usability of data for decision-making and operational processes. By implementing data quality management practices, organizations can identify and address issues such as inconsistencies, errors, and redundancies in data, ensuring that data is fit for purpose and meets the required standards. This enhances the trustworthiness of data and improves the overall effectiveness of data governance initiatives.
Implementing Data Governance in Enterprises: Data Governance For Enterprises

Implementing data governance in a large enterprise is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Below are the steps organizations can follow to successfully implement data governance, along with challenges they may face and best practices for a smooth implementation.
Financial reporting dashboards play a crucial role in helping businesses analyze their financial data efficiently. By utilizing financial reporting dashboards , companies can track key performance indicators and make informed decisions based on real-time information. These tools provide a visual representation of complex financial data, making it easier for stakeholders to understand the financial health of the organization.
Steps for Implementing Data Governance
- Establish a Data Governance Team: Create a dedicated team with representatives from different departments to oversee the data governance initiative.
- Define Data Governance Objectives: Clearly Artikel the goals and objectives of the data governance program to ensure alignment with the organization’s overall strategy.
- Assess Current Data Landscape: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the existing data landscape to identify gaps, issues, and opportunities for improvement.
- Develop Data Governance Policies: Create and document data governance policies, procedures, and guidelines to govern data usage, quality, security, and compliance.
- Implement Data Governance Tools: Invest in data governance tools and technologies to automate data management processes, monitor data quality, and ensure compliance.
- Define Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of data stewards, data owners, and other stakeholders involved in data governance.
- Establish Data Quality Metrics: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and data quality metrics to measure the effectiveness of the data governance program.
- Monitor and Improve Continuously: Continuously monitor data governance processes, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to enhance data governance maturity.
Challenges in Implementing Data Governance
- Lack of Executive Sponsorship: Without strong support from senior leadership, data governance initiatives may struggle to gain traction and resources.
- Data Silos and Fragmentation: Data scattered across different systems and departments can hinder data governance efforts and lead to inconsistent or incomplete data management.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new data governance policies and procedures, especially if they perceive them as cumbersome or restrictive.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Meeting complex data privacy regulations and compliance standards can pose challenges for data governance implementation.
Best Practices for Successful Data Governance Implementation
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders from across the organization in the data governance process to ensure buy-in and collaboration.
- Start Small, Scale Gradually: Begin with a pilot project or a specific data domain before scaling up the data governance program to the entire organization.
- Communicate Effectively: Clearly communicate the benefits of data governance to employees and stakeholders to foster a culture of data accountability and transparency.
- Provide Ongoing Training: Offer training and support to employees to help them understand their roles and responsibilities in data governance and encourage compliance.
Data Governance Tools and Technologies

Data governance tools and technologies play a crucial role in helping enterprises manage and protect their data assets effectively. These tools are designed to streamline data governance processes, ensure compliance with regulations, and improve data quality across the organization.
Popular Tools and Technologies
- Data Catalogs: Data catalogs are essential tools that provide a centralized inventory of all data assets within an organization. They help data stewards and data users discover, understand, and access relevant data quickly.
- Metadata Management Tools: Metadata management tools help organizations capture, store, and manage metadata associated with their data assets. This metadata includes information about the data’s structure, origin, quality, and usage.
- Data Quality Tools: Data quality tools help enterprises monitor and improve the quality of their data by identifying and resolving issues such as duplicates, inconsistencies, and inaccuracies.
- Data Security Tools: Data security tools are essential for protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, and safeguarding against cyber threats.
Role of Automation in Data Governance
Automation plays a significant role in enhancing data governance processes by reducing manual effort, improving efficiency, and ensuring consistency. Automated data governance tools can help organizations automate data profiling, data lineage, data classification, and other data management tasks. By automating routine data governance activities, enterprises can free up resources to focus on more strategic initiatives and ensure data governance best practices are consistently applied across the organization.
Compliance and Regulatory Aspects of Data Governance

Data governance plays a crucial role in helping enterprises comply with various regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and others. By implementing robust data governance practices, organizations can ensure that they adhere to the specific requirements Artikeld in these regulations, thereby avoiding potential fines and legal consequences.
Importance of Data Governance in Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
One of the primary reasons why data governance is essential for enterprises is its role in safeguarding data security and privacy. Through proper data governance frameworks, organizations can establish clear guidelines and protocols for handling sensitive information, ensuring that data is protected from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. This not only helps in maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders but also mitigates the risks associated with data breaches and regulatory non-compliance.
- Data Classification: Data governance helps in categorizing data based on its sensitivity and criticality, enabling organizations to apply appropriate security measures and access controls to protect sensitive information.
- Data Retention Policies: By defining data retention policies as part of their governance framework, enterprises can ensure compliance with regulations that specify how long data should be retained and when it should be securely disposed of.
- Data Access Controls: Implementing data governance allows organizations to control who can access, modify, and delete data, reducing the risk of unauthorized activities and ensuring that data is only accessed by authorized personnel.
Examples of Regulatory Requirements Impacting Data Governance Strategies
Various regulatory requirements have a direct impact on the data governance strategies adopted by enterprises. For instance, GDPR mandates that organizations must obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their personal data, necessitating the implementation of strict data governance measures to ensure compliance. Similarly, HIPAA requires healthcare organizations to protect the privacy and security of patients’ health information, leading to the establishment of comprehensive data governance frameworks to safeguard sensitive medical data.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Organizations that handle payment card data are required to comply with PCI DSS, which includes implementing robust data governance practices to secure cardholder information and prevent data breaches.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act: The Sarbanes-Oxley Act mandates that public companies must establish internal controls and procedures for financial reporting, highlighting the importance of data governance in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial data.
- FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act): Educational institutions must comply with FERPA regulations to protect the privacy of student records, emphasizing the need for data governance to secure sensitive educational data and maintain compliance with the law.
In conclusion, data governance plays a crucial role in safeguarding data, ensuring regulatory compliance, and fostering trust in data-driven decision-making processes. By embracing best practices and leveraging advanced technologies, enterprises can navigate the complexities of data governance successfully.
Understanding the data mining process steps is essential for businesses looking to extract valuable insights from large datasets. This systematic approach involves data collection, processing, and analysis to uncover patterns and trends. By following the data mining process steps, organizations can gain a competitive edge by making data-driven decisions that drive growth and innovation.
Data visualization in business is a powerful tool for presenting complex information in a clear and concise manner. By using visual elements such as charts, graphs, and maps, businesses can communicate insights effectively to stakeholders. Data visualization in business helps improve decision-making processes by enabling users to identify trends, patterns, and outliers within their data, leading to more informed strategic decisions.