Data security best practices sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with brimming originality from the outset.
In today’s digital landscape, the importance of safeguarding data is paramount to protect sensitive information from potential threats. Implementing robust data security practices is not just a choice but a necessity for organizations striving to build trust and credibility with their customers.
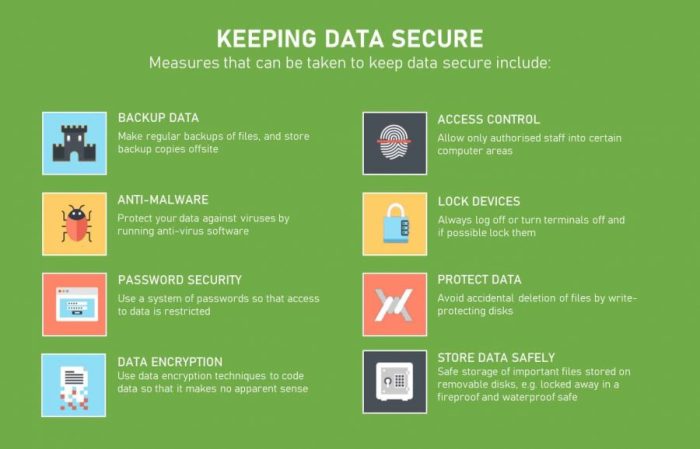
Importance of Data Security Best Practices

In today’s digital landscape, data security best practices are more crucial than ever. With the increasing amount of sensitive information being stored and transmitted online, organizations must prioritize the protection of their data to safeguard against cyber threats and breaches.
Data security best practices help prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber attacks that can have severe consequences for businesses. For example, a data breach can result in financial losses, damage to reputation, legal penalties, and loss of customer trust. By implementing robust data security measures, organizations can mitigate these risks and protect their valuable assets.
Building Trust with Customers
Implementing data security best practices not only protects organizations from potential threats but also helps build trust with customers. When customers know that their personal information is secure and protected, they are more likely to engage with a business and share their data. This trust is essential for maintaining long-term relationships with customers and fostering loyalty.
- Encrypting sensitive data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Implementing multi-factor authentication for an added layer of security.
- Regularly updating security protocols and software to address vulnerabilities.
- Training employees on data security best practices to reduce human error.
Common Threats to Data Security

Data security is constantly under threat from various malicious activities that can compromise sensitive information. It is crucial for individuals and organizations to be aware of these common threats to protect their data effectively.
Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, is a common threat to data security. It includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware that can infect computers and networks, leading to data breaches and unauthorized access to confidential information. Malware can spread through email attachments, software downloads, or malicious websites, making it essential to have robust antivirus and anti-malware programs in place.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of cyber attack where attackers impersonate legitimate entities to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, or personal details. Phishing emails, messages, or websites often appear authentic, making it challenging for users to identify them as fraudulent. It is crucial to educate employees and individuals about phishing techniques and implement email filters and security protocols to prevent falling victim to these attacks.
Social Engineering
Social engineering is a tactic used by cybercriminals to manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise data security. Attackers may use psychological manipulation, deception, or impersonation to gain access to sensitive data. It is essential to train employees on recognizing social engineering tactics and establish strict access controls and verification procedures to prevent unauthorized access to critical systems and information.
Importance of Staying Updated
To effectively mitigate the risks posed by these common threats to data security, it is crucial to stay updated on emerging trends and evolving techniques used by cybercriminals. Regularly updating security software, implementing security patches, conducting security audits, and providing ongoing cybersecurity training to employees are essential practices to safeguard data and prevent security breaches.
Best Practices for Data Encryption
Data encryption plays a vital role in securing sensitive information by converting it into a coded form that can only be accessed with the correct decryption key. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they cannot make sense of it without the key.
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption involves using a single key to both encrypt and decrypt the data. This method is fast and efficient, making it ideal for securing large volumes of data. Popular symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard).
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, uses a pair of keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method is commonly used for secure communication over the internet, such as in SSL/TLS protocols. Examples of asymmetric encryption algorithms include RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography).
Tools for Data Encryption
There are several tools and software available for implementing data encryption. Some popular options include:
– VeraCrypt: An open-source encryption tool that can create encrypted containers or encrypt entire drives.
– BitLocker: A built-in encryption tool in Windows operating systems for encrypting hard drives.
– GPG (GNU Privacy Guard): A free and open-source encryption software for secure communication and file encryption.
Implementing Access Controls: Data Security Best Practices
Access controls play a crucial role in ensuring data security by limiting who can access sensitive information within an organization. By implementing access controls, businesses can prevent unauthorized users from viewing, modifying, or deleting data, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a method of restricting network access based on the roles of individual users within an organization. Each user is assigned a specific role, and access privileges are granted based on the user’s role. This ensures that users only have access to the information necessary for their job function, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
Mandatory Access Control (MAC) is a security measure that restricts access to data based on the security clearance level of users and the classification of the data. Users are only able to access data that falls within their security clearance level, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information. MAC is commonly used in government and military settings to ensure the protection of classified data.
Regular Review and Updating of Access Control Policies
It is essential for organizations to regularly review and update their access control policies to adapt to changing security threats and organizational needs. Regular reviews help identify any gaps or vulnerabilities in the existing access controls and allow for adjustments to be made to strengthen security measures. By staying proactive and keeping access control policies up to date, businesses can better protect their data from potential security breaches.
Secure Data Backup Strategies

Data backup is a critical component of data security, ensuring that in the event of a cyberattack, hardware failure, or human error, important information can be recovered. Implementing secure data backup strategies is essential to protect sensitive data from loss or unauthorized access.
Cloud Backup, Data security best practices
- Cloud backup involves storing data on remote servers accessed through the internet. This method provides scalability, accessibility, and automated backups, reducing the risk of data loss due to physical damage or theft.
- Choose a reputable cloud service provider with robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, to safeguard your backup data.
- Ensure data encryption during transmission and storage to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Offline Backup
- Offline backup involves storing data on physical storage devices like external hard drives, USB drives, or tapes. This method provides an extra layer of security by keeping data offline and inaccessible to cyber threats.
- Regularly update offline backups and store them in a secure location away from the primary data source to protect against ransomware attacks or natural disasters.
- Implement encryption on offline backup devices and restrict physical access to prevent data breaches or theft.
Remote Backup
- Remote backup involves replicating data to a separate location, such as a secondary data center or a remote server. This method ensures data redundancy and availability in case of primary data center failure.
- Establish secure connections for remote backups using VPNs, secure FTP, or encrypted protocols to protect data during transmission over the network.
- Regularly test remote backup systems to ensure data integrity and accessibility, and update backup procedures based on changing business needs or regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, embracing data security best practices is not only a proactive approach to safeguarding valuable information but also a strategic move towards establishing a secure environment for data management. By adhering to these practices diligently, organizations can mitigate risks effectively and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data.
Are you new to the world of machine learning and looking to get started with TensorFlow? Check out this comprehensive guide on TensorFlow for beginners to kickstart your journey in building neural networks and deep learning models.
Looking for the best tools to visualize your data effectively? Explore our list of top data visualization tools that can help you create stunning charts, graphs, and dashboards to communicate your insights clearly.
Enterprises can leverage the power of visual analytics to gain valuable insights from their data. Discover how visual analytics for enterprises can help you make informed decisions and drive business growth.